Giới thiệu
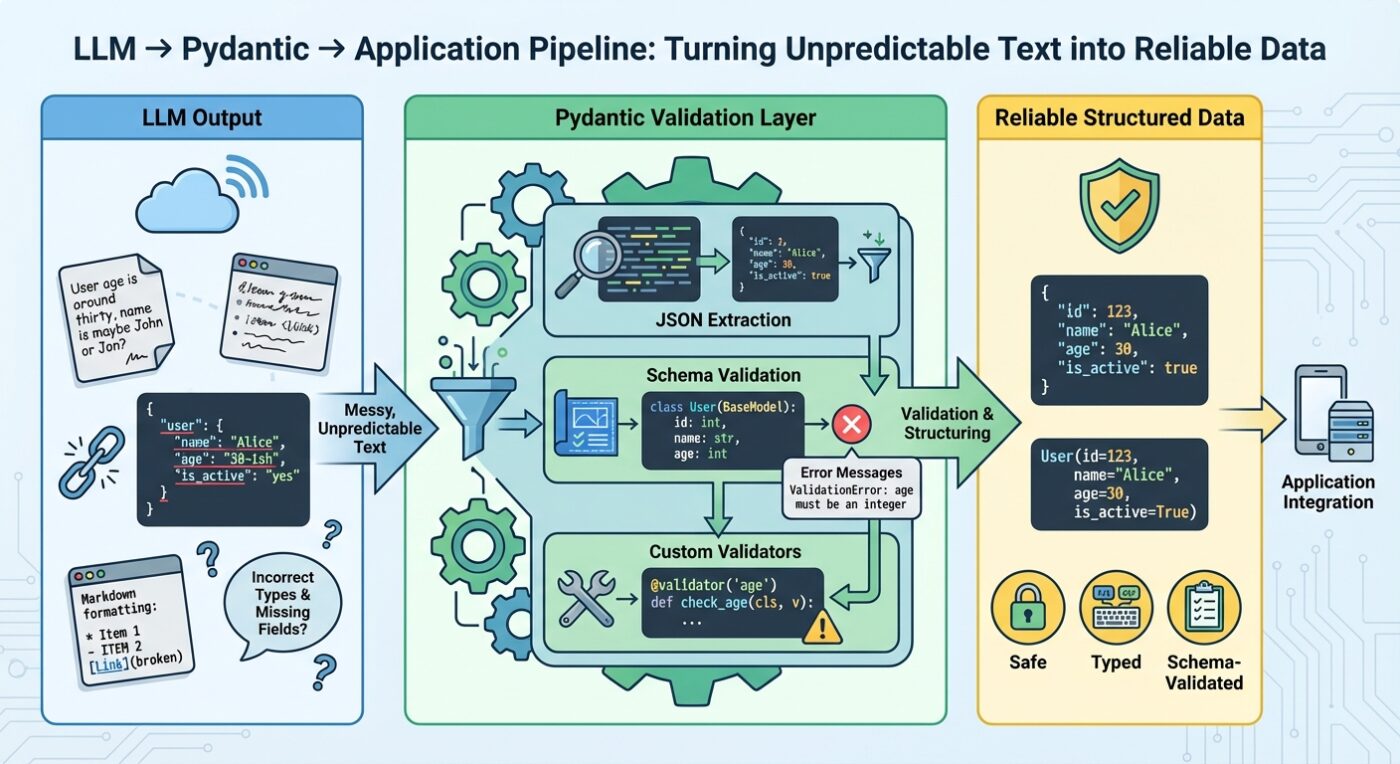
Các mô hình ngôn ngữ lớn (LLM) chủ yếu sinh ra văn bản tự do, chứ không phải dữ liệu có cấu trúc. Dù bạn đã hướng dẫn LLM trả về dữ liệu dạng JSON, thực tế nó chỉ tạo ra văn bản trông giống như JSON hợp lệ. Đầu ra này có thể sai tên trường, thiếu trường cần thiết, kiểu dữ liệu không đúng, hoặc bị kèm thêm văn bản mô tả xung quanh. Nếu không kiểm tra và xác thực, các lỗi này có thể khiến chương trình của bạn bị lỗi hoặc khó phát hiện nguyên nhân.
Pydantic là công cụ xác thực dữ liệu theo kiểu động dựa trên chú thích kiểu dữ liệu Python. Nó giúp kiểm tra đầu ra từ LLM có đúng với cấu trúc mong muốn không, tự động chuyển đổi kiểu khi có thể, và trả về thông báo lỗi rõ ràng khi gặp vấn đề. Nhờ đó, bạn thiết lập được một “cam kết” rõ ràng giữa kết quả LLM và yêu cầu của ứng dụng.
Bài viết này sẽ hướng dẫn cách sử dụng Pydantic để xác thực đầu ra từ LLM: từ định nghĩa lược đồ xác thực, xử lý các trường hợp phản hồi sai định dạng, dữ liệu lồng nhau, kết nối với API LLM, cách thử lại khi xác thực thất bại, và nhiều mẹo khác. Hãy cùng bắt đầu nhé.
🔗 Bạn có thể tham khảo mã nguồn ví dụ tại GitHub. Trước khi thực hành, hãy cài đặt Pydantic bản 2.x và các phụ thuộc email:
pip install pydantic[email].
Khởi Đầu Nhanh
Ví dụ đơn giản đầu tiên: xây dựng trình trích xuất thông tin liên hệ từ một đoạn văn bản. LLM sẽ đọc văn bản không cấu trúc và trả về dữ liệu có cấu trúc, sau đó bạn xác thực bằng Pydantic:
from pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStr, field_validator
from typing import Optional
class ContactInfo(BaseModel):
name: str
email: EmailStr
phone: Optional[str] = None
company: Optional[str] = None
@field_validator('phone')
@classmethod
def validate_phone(cls, v):
if v is None:
return v
cleaned = ''.join(filter(str.isdigit, v))
if len(cleaned) < 10:
raise ValueError('Số điện thoại phải có ít nhất 10 chữ số')
return cleaned
Mọi mô hình Pydantic kế thừa từ BaseModel đều tự động kiểm tra kiểu dữ liệu dựa trên chú thích kiểu. Kiểu EmailStr giúp kiểm tra định dạng email mà không cần viết biểu thức chính quy riêng. Các trường kiểu Optional[str] = None nghĩa là có thể bỏ trống hoặc không có giá trị. Hàm trang trí @field_validator cho phép bạn bổ sung logic kiểm tra riêng, ví dụ chuẩn hóa số điện thoại và kiểm tra độ dài.
Cách xác thực đầu ra từ LLM với mô hình này:
import json
llm_response = '''
{
"name": "Sarah Johnson",
"email": "[email protected]",
"phone": "(555) 123-4567",
"company": "TechCorp Industries"
}
'''
data = json.loads(llm_response)
contact = ContactInfo(**data)
print(contact.name)
print(contact.email)
print(contact.model_dump())
Khi khởi tạo ContactInfo, mọi trường sẽ được kiểm tra tự động. Nếu có lỗi, bạn sẽ nhận được thông báo cụ thể chỉ ra vấn đề.
Xử Lý Và Kiểm Tra Đầu Ra LLM Không Chuẩn
LLM không phải lúc nào cũng trả về JSON đúng chuẩn. Đôi khi còn kèm thêm văn bản mô tả, Markdown, hoặc sai cấu trúc. Dưới đây là cách xử lý các trường hợp này:
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError, field_validator
import json
import re
class ProductReview(BaseModel):
product_name: str
rating: int
review_text: str
would_recommend: bool
@field_validator('rating')
@classmethod
def validate_rating(cls, v):
if not 1 <= v <= 5:
raise ValueError('Điểm đánh giá phải là số nguyên từ 1 đến 5')
return v
def extract_json_from_llm_response(response: str) -> dict:
"""Tách khối JSON từ phản hồi LLM có thể kèm văn bản ngoài lề."""
json_match = re.search(r'\{.*\}', response, re.DOTALL)
if json_match:
return json.loads(json_match.group())
raise ValueError("Không tìm thấy JSON trong phản hồi")
def parse_review(llm_output: str) -> ProductReview:
"""Phân tích và xác thực đầu ra LLM đảm bảo an toàn."""
try:
data = extract_json_from_llm_response(llm_output)
review = ProductReview(**data)
return review
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Lỗi phân tích JSON: {e}")
raise
except ValidationError as e:
print(f"Lỗi xác thực: {e}")
raise
except Exception as e:
print(f"Lỗi khác: {e}")
raise
Phương pháp này sử dụng regex để tìm khối JSON trong phản hồi, giải quyết trường hợp LLM kèm thêm mô tả ngoài dữ liệu. Bắt riêng từng loại lỗi để xử lý:
JSONDecodeErrorkhi dữ liệu JSON không hợp lệ,ValidationErrorcho dữ liệu sai cấu trúc,- và xử lý ngoại lệ khác bất ngờ.
Hàm extract_json_from_llm_response chịu trách nhiệm làm sạch văn bản, còn parse_review lo xác thực dữ liệu, tách biệt rõ ràng từng nhiệm vụ. Khi áp dụng thực tế, bạn nên bổ sung ghi log lỗi hoặc thử lại với prompt có hướng dẫn bổ sung.
Ví dụ với đầu ra LLM có kèm văn bản mô tả:
messy_response = '''
Here's the review in JSON format:
{
"product_name": "Wireless Headphones X100",
"rating": 4,
"review_text": "Great sound quality, comfortable for long use.",
"would_recommend": true
}
Hope this helps!
'''
review = parse_review(messy_response)
print(f"Sản phẩm: {review.product_name}")
print(f"Đánh giá: {review.rating}/5")
Trình phân tích sẽ tự động tách lấy khối JSON và xác thực theo mô hình ProductReview.
Xử Lý Dữ Liệu Lồng Nhau
Trong thực tế, dữ liệu thường có cấu trúc lồng nhau. Dưới đây là cách xác thực dữ liệu đa cấp như sản phẩm có nhiều thông số kỹ thuật và đánh giá:
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, field_validator
from typing import List
class Specification(BaseModel):
key: str
value: str
class Review(BaseModel):
reviewer_name: str
rating: int = Field(..., ge=1, le=5)
comment: str
verified_purchase: bool = False
class Product(BaseModel):
id: str
name: str
price: float = Field(..., gt=0)
category: str
specifications: List[Specification]
reviews: List[Review]
average_rating: float = Field(..., ge=1, le=5)
@field_validator('average_rating')
@classmethod
def check_average_matches_reviews(cls, v, info):
reviews = info.data.get('reviews', [])
if reviews:
calculated_avg = sum(r.rating for r in reviews) / len(reviews)
if abs(calculated_avg - v) > 0.1:
raise ValueError(
f'Điểm trung bình {v} không khớp với giá trị tính toán {calculated_avg:.2f}'
)
return v
Mô hình Product chứa danh sách Specification và Review, mỗi cấu trúc con sẽ được xác thực tự động. Sử dụng Field(..., ge=1, le=5) có thể đặt ràng buộc giá trị ngay trong mô hình. Hàm kiểm tra check_average_matches_reviews có thể truy cập các trường liên quan để xác thực mối quan hệ logic giữa chúng.
Khi truyền dictionary lồng nhau vào Product(**data), Pydantic sẽ tự động xây dựng các đối tượng Specification và Review bên trong.
Ví dụ xác thực dữ liệu sản phẩm hoàn chỉnh:
llm_response = {
"id": "PROD-2024-001",
"name": "Smart Coffee Maker",
"price": 129.99,
"category": "Kitchen Appliances",
"specifications": [
{"key": "Capacity", "value": "12 cups"},
{"key": "Power", "value": "1000W"},
{"key": "Color", "value": "Stainless Steel"}
],
"reviews": [
{
"reviewer_name": "Alex M.",
"rating": 5,
"comment": "Makes excellent coffee every time!",
"verified_purchase": True
},
{
"reviewer_name": "Jordan P.",
"rating": 4,
"comment": "Good but a bit noisy",
"verified_purchase": True
}
],
"average_rating": 4.5
}
product = Product(**llm_response)
print(f"{product.name}: ${product.price}")
print(f"Đánh giá trung bình: {product.average_rating}")
print(f"Số lượng đánh giá: {len(product.reviews)}")
Pydantic sẽ kiểm tra toàn bộ cấu trúc lồng nhau chỉ với một lần xác thực.
Kết Hợp Pydantic Với API LLM Và Các Framework
Bạn cần một phương pháp đáng tin cậy để chuyển đổi văn bản tự do sang dữ liệu có cấu trúc đã xác thực. Dưới đây là cách sử dụng Pydantic cùng API OpenAI, cũng như các framework như LangChain và LlamaIndex. Đảm bảo bạn đã cài những SDK cần thiết.
Kết hợp Pydantic với OpenAI API
Ví dụ trích xuất thông tin sách từ văn bản tự do, xác thực bằng Pydantic:
from openai import OpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List
import os
client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
class BookSummary(BaseModel):
title: str
author: str
genre: str
key_themes: List[str]
main_characters: List[str]
brief_summary: str
recommended_for: List[str]
def extract_book_info(text: str) -> BookSummary:
"""Trích xuất thông tin sách có cấu trúc từ văn bản tự do."""
prompt = f"""
Extract book information from the following text and return it as JSON.
Required format:
{{
"title": "book title",
"author": "author name",
"genre": "genre",
"key_themes": ["theme1", "theme2"],
"main_characters": ["character1", "character2"],
"brief_summary": "summary in 2-3 sentences",
"recommended_for": ["audience1", "audience2"]
}}
Text: {text}
Return ONLY the JSON, no additional text.
"""
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant that extracts structured data."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
],
temperature=0
)
llm_output = response.choices[0].message.content
import json
data = json.loads(llm_output)
return BookSummary(**data)
Prompt chỉ rõ cấu trúc JSON mong muốn, giúp LLM trả về dữ liệu đúng với mô hình Pydantic. Đặt temperature=0 để LLM không sáng tạo ngoài yêu cầu. Luôn xác thực lại bằng Pydantic, không nên tin tưởng hoàn toàn vào đầu ra LLM.
Ví dụ trích xuất thông tin sách từ mô tả:
book_text = """
'The Midnight Library' by Matt Haig is a contemporary fiction novel that explores
themes of regret, mental health, and the infinite possibilities of life. The story
follows Nora Seed, a woman who finds herself in a library between life and death,
where each book represents a different life she could have lived. Through her journey,
she encounters various versions of herself and must decide what truly makes a life worth living.
The book resonates with readers dealing with depression, anxiety, or life transitions.
"""
try:
book_info = extract_book_info(book_text)
print(f"Tên sách: {book_info.title}")
print(f"Tác giả: {book_info.author}")
print(f"Chủ đề: {', '.join(book_info.key_themes)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Lỗi trích xuất thông tin sách: {e}")
Hàm này gửi văn bản kèm hướng dẫn định dạng rõ ràng, sau đó xác thực phản hồi bằng BookSummary.
Kết hợp LangChain với Pydantic
LangChain hỗ trợ sẵn việc trích xuất đầu ra có cấu trúc dựa trên mô hình Pydantic. Có hai cách phổ biến:
Cách thứ nhất là dùng PydanticOutputParser, tự động sinh hướng dẫn định dạng từ mô hình Pydantic:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class Restaurant(BaseModel):
"""Thông tin nhà hàng."""
name: str = Field(description="Tên nhà hàng")
cuisine: str = Field(description="Loại ẩm thực")
price_range: str = Field(description="Khoảng giá: $, $$, $$$, hoặc $$$$")
rating: Optional[float] = Field(default=None, description="Đánh giá trên thang 5")
specialties: List[str] = Field(description="Các món đặc trưng")
def extract_restaurant_with_parser(text: str) -> Restaurant:
"""Trích xuất thông tin nhà hàng bằng PydanticOutputParser của LangChain."""
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Restaurant)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Extract restaurant information from the following text.\n{format_instructions}\n{text}\n",
input_variables=["text"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
chain = prompt | llm | parser
result = chain.invoke({"text": text})
return result
Parser sẽ tự động sinh hướng dẫn định dạng từ mô hình, mô tả rõ các trường và kiểu dữ liệu, phù hợp với LLM tuân thủ tốt các chỉ dẫn.
Cách thứ hai là sử dụng with_structured_output(), tận dụng khả năng gọi hàm native của LLM:
def extract_restaurant_structured(text: str) -> Restaurant:
"""Trích xuất thông tin nhà hàng bằng with_structured_output."""
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(Restaurant)
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Extract restaurant information from the following text:\n\n{text}"
)
chain = prompt | structured_llm
result = chain.invoke({"text": text})
return result
Cách này giúp mã ngắn gọn, tận dụng tối đa khả năng function calling của mô hình để trả về dữ liệu đúng cấu trúc.
Ví dụ sử dụng:
restaurant_text = """
Mama's Italian Kitchen là nhà hàng ấm cúng thuộc sở hữu gia đình, phục vụ
ẩm thực Ý chính hiệu. Được chấm 4.5 sao, nổi tiếng với mì ống tự làm và
pizza nướng củi. Giá cả vừa phải ($$), các món đặc trưng gồm lasagna bolognese và tiramisu.
"""
try:
restaurant_info = extract_restaurant_structured(restaurant_text)
print(f"Nhà hàng: {restaurant_info.name}")
print(f"Ẩm thực: {restaurant_info.cuisine}")
print(f"Đặc sản: {', '.join(restaurant_info.specialties)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Lỗi: {e}")
Kết hợp LlamaIndex với Pydantic
LlamaIndex đặc biệt mạnh khi xử lý tài liệu lớn hoặc xây dựng hệ thống RAG, hỗ trợ nhiều phương pháp trích xuất có cấu trúc.
Cách đơn giản nhất là dùng LLMTextCompletionProgram:
from llama_index.core.program import LLMTextCompletionProgram
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class Product(BaseModel):
"""Thông tin sản phẩm."""
name: str = Field(description="Tên sản phẩm")
brand: str = Field(description="Hãng sản xuất")
category: str = Field(description="Phân loại sản phẩm")
price: float = Field(description="Giá tiền USD")
features: List[str] = Field(description="Tính năng nổi bật")
rating: Optional[float] = Field(default=None, description="Đánh giá khách hàng trên thang 5")
def extract_product_simple(text: str) -> Product:
"""Trích xuất thông tin sản phẩm với LlamaIndex."""
prompt_template_str = """
Extract product information from the following text and structure it properly:
{text}
"""
program = LLMTextCompletionProgram.from_defaults(
output_cls=Product,
prompt_template_str=prompt_template_str,
verbose=False
)
result = program(text=text)
return result
Tham số output_cls giúp xác thực tự động bằng Pydantic, phù hợp cho các bài toán trích xuất nhanh.
Khi làm việc với các mô hình hỗ trợ function calling, bạn có thể dùng FunctionCallingProgram. Nếu cần kiểm soát parsing chi tiết, hãy dùng PydanticOutputParser:
from llama_index.core.program import LLMTextCompletionProgram
from llama_index.core.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
def extract_product_with_parser(text: str) -> Product:
"""Trích xuất sản phẩm với parser chi tiết."""
prompt_template_str = """
Extract product information from the following text:
{text}
{format_instructions}
"""
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
program = LLMTextCompletionProgram.from_defaults(
output_parser=PydanticOutputParser(output_cls=Product),
prompt_template_str=prompt_template_str,
llm=llm,
verbose=False
)
result = program(text=text)
return result
Ví dụ thực tế:
product_text = """
Tai nghe không dây Sony WH-1000XM5 sở hữu khả năng chống ồn hàng đầu,
chất lượng âm thanh xuất sắc, pin lên tới 30 giờ sử dụng. Giá 399,99 USD,
đi kèm công nghệ Adaptive Sound Control, kết nối đa thiết bị,
và speak-to-chat. Khách hàng đánh giá 4.7 trên 5 sao.
"""
try:
product_info = extract_product_with_parser(product_text)
print(f"Sản phẩm: {product_info.name}")
print(f"Hãng: {product_info.brand}")
print(f"Giá: ${product_info.price}")
print(f"Tính năng: {', '.join(product_info.features)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Lỗi: {e}")
Bạn nên dùng parser chi tiết khi cần logic đặc biệt, hoặc khi mô hình không hỗ trợ function calling.
Thử Lại Khi LLM Trả Về Dữ Liệu Không Đúng
Nếu đầu ra từ LLM không hợp lệ, bạn có thể thử lại bằng cách bổ sung thông báo lỗi từ lần xác thực trước vào prompt:
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
from typing import Optional
import json
class EventExtraction(BaseModel):
event_name: str
date: str
location: str
attendees: int
event_type: str
def extract_with_retry(llm_call_function, max_retries: int = 3) -> Optional[EventExtraction]:
"""Cố gắng trích xuất dữ liệu hợp lệ với tối đa số lần thử lại kèm thông báo lỗi xác thực."""
last_error = None
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
response = llm_call_function(last_error)
data = json.loads(response)
return EventExtraction(**data)
except ValidationError as e:
last_error = str(e)
print(f"Lần thử {attempt + 1} thất bại: {last_error}")
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
print("Đã thử tối đa, dừng lại.")
return None
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"Lần thử {attempt + 1}: JSON không hợp lệ")
last_error = "The response was not valid JSON. Please return only valid JSON."
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
return None
return None
Mỗi lần thử lại sẽ kèm thông báo lỗi trước đó, giúp LLM hiểu rõ vấn đề cần xử lý. Sau số lần thử tối đa, hàm sẽ trả về None để ứng dụng chủ động xử lý.
Khi ứng dụng thực tế, hàm llm_call_function sẽ tạo prompt có nội dung: "Previous attempt failed with error: {error}. Please fix and try again."
Ví dụ LLM mô phỏng phản hồi cải thiện qua từng lần thử:
def mock_llm_call(previous_error: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
"""Mô phỏng LLM cải thiện phản hồi theo lỗi xác thực."""
if previous_error is None:
return '{"event_name": "Tech Conference 2024", "date": "2024-06-15", "location": "San Francisco"}'
elif "attendees" in previous_error.lower():
return '{"event_name": "Tech Conference 2024", "date": "2024-06-15", "location": "San Francisco", "attendees": "about 500", "event_type": "Conference"}'
else:
return '{"event_name": "Tech Conference 2024", "date": "2024-06-15", "location": "San Francisco", "attendees": 500, "event_type": "Conference"}'
result = extract_with_retry(mock_llm_call)
if result:
print(f"\nThành công! Đã trích xuất sự kiện: {result.event_name}")
print(f"Số người dự kiến: {result.attendees}")
else:
print("Không trích xuất được dữ liệu hợp lệ")
Lần thử đầu thiếu trường attendees, lần hai sai kiểu dữ liệu, lần ba đúng hết. Cơ chế thử lại sẽ giúp bạn tăng độ tin cậy cho dữ liệu.
Kết Luận
Pydantic là giải pháp chuyển đổi đầu ra LLM vốn không ổn định thành dữ liệu có cấu trúc, đảm bảo kiểm tra kiểu và logic. Kết hợp lược đồ rõ ràng cùng xử lý lỗi chặt chẽ, bạn có thể xây dựng ứng dụng AI mạnh mẽ và đáng tin cậy.
Tóm tắt:
- Xây dựng lược đồ xác thực rõ ràng phù hợp với bài toán
- Luôn xác thực dữ liệu, xử lý lỗi và thử lại khi cần thiết
- Sử dụng chú thích kiểu, validator để đảm bảo dữ liệu chuẩn xác
- Đưa lược đồ vào prompt để định hướng đầu ra LLM
Hãy bắt đầu từ mô hình đơn giản, bổ sung xác thực khi gặp trường hợp đặc biệt từ kết quả LLM. Chúc bạn thành công!
Tài Liệu Tham Khảo
- Function Calling Program for Structured Extraction | LlamaIndex Python Documentation
- Pydantic – LlamaIndex
- Structured output – Docs by LangChain
- How to Use Pydantic for LLMs – Pydantic
- Tham khảo thêm các gợi ý ChatGPT sáng tạo nội dung hay nhất của tôi